All About Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Printed From: One Stop Testing
Category: Testing Tools @ OneStopTesting
Forum Name: QuickTest Pro @ OneStopTesting
Forum Discription: QuickTest Pro is a fresh approach to automated software and application testing that addresses testing needs of both business analysts and Quality Assurance professionals.
URL: http://forum.onestoptesting.com/forum_posts.asp?TID=7033
Printed Date: 09Jan2025 at 10:40am
Topic: All About Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Posted By: Mithi25
Subject: All About Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Date Posted: 22Sep2009 at 12:52am
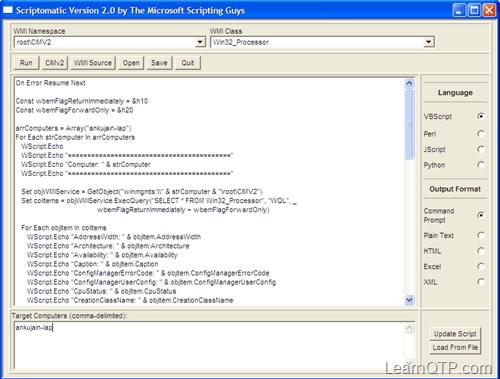
What is Windows Management Instrumentation(WMI)?WMI provides a model to represent, store and query configuration and status information of computers running Windows operating system. You can use WMI to fetch information from your system or from any other system in your network. Where can we use WMI in QTP?You can use WMI to query and retrieve information from a computer where a QTP script is running. WMI can be used for tasks like – but not limited to – finding the time zone of a machine, retrieving information about the currently running processes that you see in Windows Task Manager (Ctrl – Shift – Esc), finding physical memory (RAM), current RAM (commit charge), CPU usage etc. Here is a sample script to find the time zone of a machine. 01.Dim oWMIService, oComputer, colComputer02.Dim strComputer03. 04.strComputer = "."05. 06.Set oWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" _07.& "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\" _08.& strComputer & "\root\cimv2")09. 10.Set colComputer = oWMIService.ExecQuery _11.("Select * from Win32_TimeZone")12. 13.For Each oComputer in colComputer14. 15.msgbox oComputer.Description16. 17.Exit For18.Next19. 20.Set oComputer = Nothing21.Set colComputer = Nothing22.Set oWMIService = NothingLet us see what the statements above mean:
Output for the script above would look something like this:
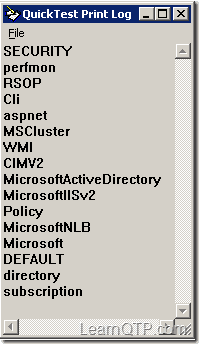
What do we mean by namespace?Namespace in WMI can be defined as a logical database of classes and their instances. The parent of all namespaces is the root. Here is a sample script to get all namespaces contained inside root. 1.Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:\\.\root")2.Set colNamespaces = objWMIService.InstancesOf("__NAMESPACE")3. 4.For Each objNamespace In colNamespaces5.print objNamespace.Name6.Next
root\CIMV2 is the default WMI namespace. So, the first script would work fine even with this statement: 1.Set oWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" _2.& "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\”)Which namespace is required for us?As QTP developer, we would be working with CIMV2 workspace. So, we can consider this part to remain the same while writing WMI scripts. 1.Set oWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" _2.& "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\" _3.& strComputer & "\root\cimv2")How to write scripts in WMI?
How to identify which class and which property we want?There is no straightforward answer for this question. Knowledge
about classes and corresponding properties comes with experience.
Having said that, the names assigned to various classes are quite
meaningful. One way is to think of what name you would assign to a
given class if you were the developer. ------------- http://www.quick2sms.com - Send Unlimited FREE SMS to Any Mobile Anywhere in INDIA, Click Here |
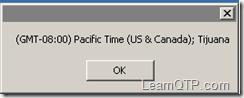 You can copy the above code into a .vbs file to get the time zone of your machine.
You can copy the above code into a .vbs file to get the time zone of your machine.